Understanding Thalassemia: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Welcome to Recmed Medical's comprehensive guide to Thalassemia, a group of inherited blood disorders impacting hemoglobin production. Our goal is to provide valuable insights into the causes, types, symptoms, and available treatment options for individuals affected by Thalassemia.
Introduction:
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that results in reduced hemoglobin production. Hemoglobin plays a vital role in carrying oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. When hemoglobin production is affected, individuals may experience anemia, fatigue, and various complications. At Recmed Medical, our team of medical experts is dedicated to offering accurate and in-depth information about Thalassemia, empowering individuals with knowledge about this condition.
Causes and Types:
Thalassemia is primarily caused by genetic mutations affecting the genes responsible for hemoglobin production. These mutations lead to a disruption in the normal hemoglobin synthesis process. There are two main types of Thalassemia: Alpha Thalassemia and Beta Thalassemia, each further classified into subtypes. The specific mutations determine the severity and clinical presentation of the condition. Our Genetic Counselors specialize in providing personalized insights into specific Thalassemia types, helping individuals understand their condition and its implications.
Symptoms and Complications:
Thalassemia symptoms can vary widely based on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). In more severe cases, individuals may experience delayed growth and development, bone deformities, and an enlarged spleen. The severity of symptoms depends on factors such as the type of Thalassemia and the presence of other coexisting conditions. Early recognition of symptoms is key to seeking timely medical intervention and managing potential complications.
Diagnosis and Screening:
Accurate diagnosis of Thalassemia involves a series of blood tests to measure hemoglobin levels and identify abnormal hemoglobin variants. Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a common diagnostic test that helps distinguish different types of Thalassemia based on the hemoglobin patterns. Additionally, genetic testing plays a crucial role in confirming the type and severity of Thalassemia by identifying specific mutations in the responsible genes. Our advanced diagnostic techniques and collaborations with leading laboratories ensure precise Thalassemia diagnoses, enabling tailored treatment plans.
Treatment Approaches:
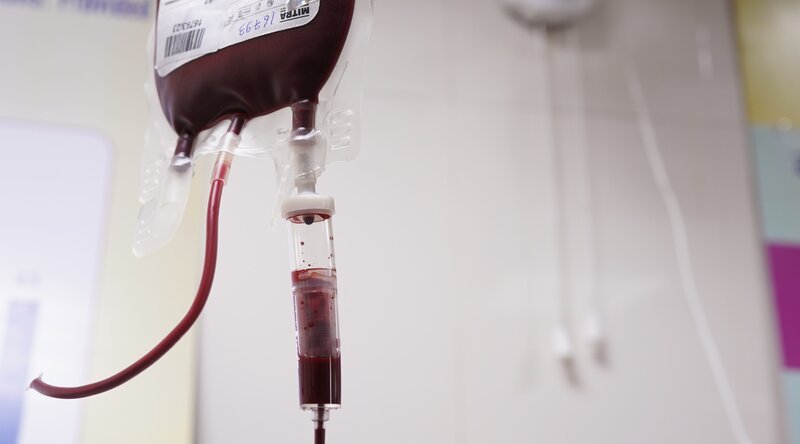
The treatment approach for Thalassemia varies depending on the type and severity of the condition. In milder cases, individuals may only require occasional blood transfusions to manage anemia and maintain hemoglobin levels. However, individuals with more severe forms of Thalassemia may require regular blood transfusions to alleviate anemia symptoms and provide a stable supply of healthy red blood cells. Over time, repeated blood transfusions can lead to an excess of iron in the body, requiring chelation therapy to remove the excess iron and prevent related complications. In some cases, bone marrow transplantation may be considered as a potential cure for Thalassemia. Our collaborative team of Hematologists, Specialists, and Medical Professionals work closely with patients to design personalized treatment plans that address their unique needs and circumstances.
Quality of Life and Support:
Living with Thalassemia presents physical and emotional challenges for individuals and their families. Beyond medical care, Recmed Medical is dedicated to enhancing the overall quality of life for those affected by Thalassemia. We provide a range of support services, including educational resources, psychological counseling, and connections to support groups. These resources aim to improve mental well-being, provide coping strategies, and foster a sense of community among individuals facing similar challenges.
Recmed Medical's Dedication:
At Recmed Medical, our commitment extends beyond providing accurate information and medical treatment. We understand the impact Thalassemia has on individuals and families, and we're dedicated to providing accessible and comprehensive healthcare services. Through collaborations with leading Thalassemia centers, we ensure that patients receive optimal care, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing support. Our dedication is rooted in making healthcare accessible and empowering those impacted by Thalassemia to lead fulfilling lives.
Conclusion: Empowering Individuals with Thalassemia:
Understanding Thalassemia empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and treatment journey. At Recmed Medical, our experts are here to provide the necessary guidance, support, and medical expertise for individuals and families navigating the challenges of Thalassemia. Together, we can improve the lives of those affected by this condition by fostering knowledge, compassion, and comprehensive healthcare solutions.
By Recmed Medical – Hematology Professors (Click this link to connect with our Hematology Doctors)
References:
- Cohen, Alan R., et al. "Thalassemia." ASH Education Program Book 2004.1 (2004): 14-34.
- Galanello, Renzo, and Raffaella Origa. "Beta-thalassemia." Orphanet journal of rare diseases 5 (2010): 1-15.
- Cao, Antonio, and Renzo Galanello. "Beta-thalassemia." Genetics in medicine 12.2 (2010): 61-76.
- Rund, Deborah, and Eliezer Rachmilewitz. "β-Thalassemia." New England Journal of Medicine 353.11 (2005): 1135-1146.
- Rachmilewitz, Eliezer A., and Patricia J. Giardina. "How I treat thalassemia." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 118.13 (2011): 3479-3488.
- Muncie Jr, Herbert L., and James S. Campbell. "Alpha and beta thalassemia." American family physician 80.4 (2009): 339-344.
- Schrier, Stanley L. "Pathophysiology of thalassemia." Current opinion in hematology 9.2 (2002): 123-126.
- Vichinsky, Elliott P. "Changing patterns of thalassemia worldwide." Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences1054.1 (2005): 18-24.
- Aydinok, Yesim. "Thalassemia." Hematology 17.sup1 (2012): s28-s31.
- Cao, Antonio, and Yuet Wai Kan. "The prevention of thalassemia." Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine 3.2 (2013).
- Taher, Ali, Hussain Isma'eel, and Maria D. Cappellini. "Thalassemia intermedia: revisited." Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases 37.1 (2006): 12-20.
LATEST NEWS
Blog Posts